People who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result in illnesses and injuries. Heat stress can result in heat stroke, heat exhaustion, heat cramps, or heat rashes. Heat can also increase the risk of injuries as it may result in sweaty palms, fogged-up glasses, and dizziness. Burns may also occur as a result of accidental contact with hot surfaces or steam.
People at risk of heat stress include people who enjoy the outdoors and workers in hot environments such as firefighters, bakery workers, farmers, construction workers, miners, boiler room workers, factory workers, and others.
People at greater risk of heat stress include those who are 65 years of age or older, are overweight, have heart disease or high blood pressure, or take medications that may be affected by extreme heat.
Prevention of heat stress is important. Everyone should understand what heat stress is, how it affects their health and safety, and how it can be prevented. It is also imperative to know how to identify the signs of onset heat stress. Below are some ways to identify heat exhaustion and heat stroke, as well as how to address these conditions.
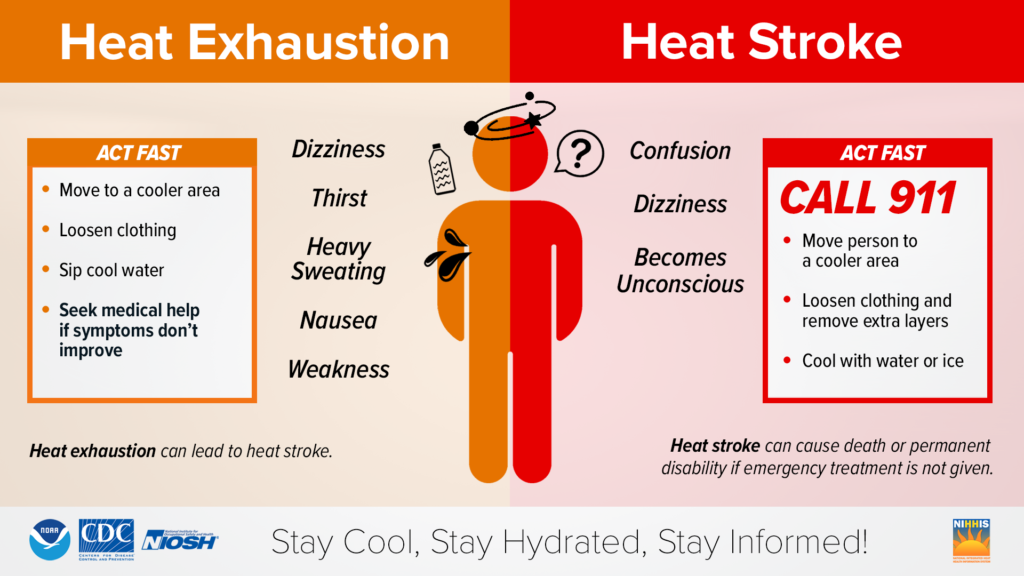
Heat ExhaustionHeat exhaustion is the body’s response to an excessive loss of water and salt, usually through excessive sweating. Heat exhaustion is most likely to affect:
SymptomsSymptoms of heat exhaustion include:
First AidTreat a worker who has heat exhaustion by doing the following:
|
Heat StrokeHeat stroke is the most serious heat-related illness. It occurs when the body can no longer control its temperature: the body’s temperature rises rapidly, the sweating mechanism fails, and the body is unable to cool down. When heat stroke occurs, the body temperature can rise to 106°F or higher within 10 to 15 minutes. Heat stroke can cause permanent disability or death if the person does not receive emergency treatment. SymptomsSymptoms of heat stroke include:
First AidTake the following steps to treat a worker with heat stroke:
|