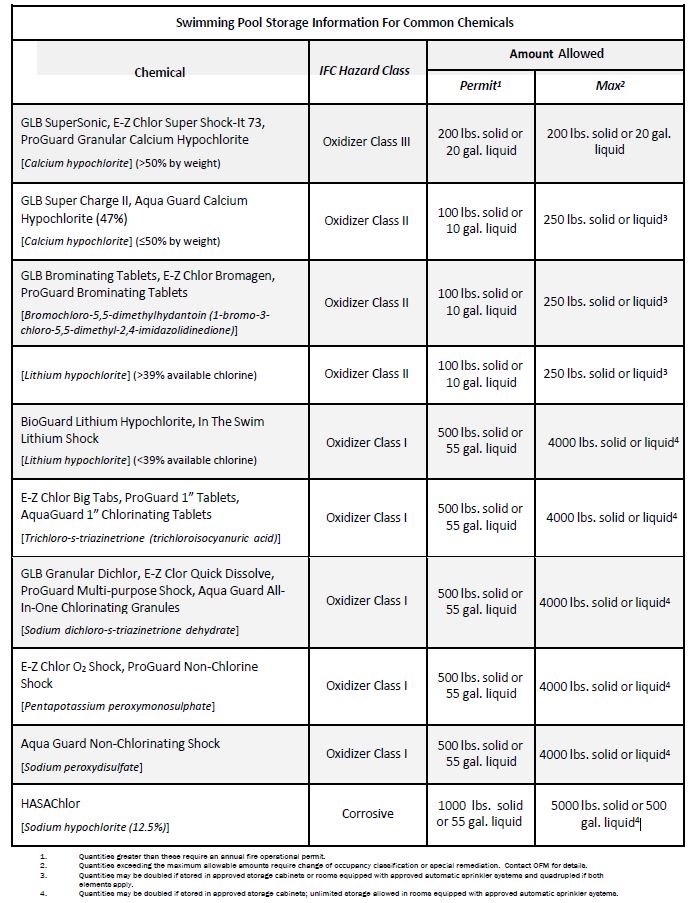
SAFE USE OF SWIMMING POOL CHEMICALS
COMMON POOL CHEMICALS contain health and safety hazards and should be handled with caution. Improper storage and use may result in explosive compounds, toxic gases or damage to skin and eyes.
The following are some guidelines for safe storage and use of swimming pool chemicals:
- Keep storage room well ventilated. Mechanical ventilation shall be provided if natural ventilation is insufficient.(1) Storage must also remain cool(2) and out of direct sunlight.(3)
- Liquids shall not be stored above dry chemicals.(4)
- Keep dry chemicals dry.(5) Keep bags off the floor. Keep chemicals secure and closed in their original packaging.
- Incompatible materials (below) in containers greater than 5 lbs. or 0.5 gal. shall be segregated. Separation may be accomplished by: keeping incompatible materials no less than 20 ft. apart; placing a noncombustible partition between incompatible materials extending no less than 18 in. above and to the sides of the stored material; storing liquid and solid materials in hazardous material storage cabinets.(6)
- Hazard identification signs as specified in NFPA 704 shall be placed at entrance to storage rooms requiring a permit.(7)
- And remember—Always follow manufacturer’s directions carefully for storage and use; use proper personal protective equipment (PPE)!
- 2015 International Fire Code 5004.3
- National Fire Protection Association Standard 430 Section D.3.1
- IFC 5003.9.6
- NFPA 430 Section 9.2.2
- NFPA 430 Section D.3.1
- IFC 5003.9.8
- IFC 5003.5

Incompatible Materials?
Oxidizers may keep our pools clean and clear, but are very dangerous if mishandled.
Oxidizers are incompatible with many materials including acids (muriatic and hypochloric), bases, carbonated beverages, paints, floor sweeping compounds, common household cleaners or degreasers, many algaecides such as quats, and even other oxidizers.
Chlorine is a reactive chemical!
Dangerous reactions and fumes may result if mixed with other chemicals. Calcium hypochlorite, for instance, can release toxic chlorine gas and heat sufficient to ignite combustibles merely by becoming wet.